At VUBU-MEDICAL you can order surgical instruments in certified medical quality online. We supply hospitals, medical practices and surgical centers with precision instruments made of corrosion-resistant stainless steel. All instruments are CE-marked, autoclavable and designed for repeated sterilization cycles in daily clinical use.
The portfolio includes basic and specialized instruments for diagnostics, dissection, hemostasis and suturing in more than 30,000 variants for human and veterinary medicine.
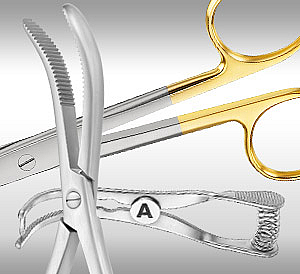
Surgical instruments are used for cutting, grasping, holding, spreading, puncturing and suturing tissue. Shape, length and jaw profile vary depending on specialty and surgical depth.
All instruments are manufactured from hardened medical stainless steel and comply with DIN ISO 13485 and European medical device regulations. Each instrument is inspected before shipping for functionality, alignment and surface quality.
The selection depends on tissue type and procedure. Important criteria include:
All items include dimensions and technical data and can be found via categories or full-text search.
Surgical instruments are precision tools designed to perform specific actions during medical procedures such as cutting, grasping, clamping, retracting or suturing tissue. Modern instruments are manufactured from corrosion-resistant stainless steel, autoclavable and optimized for repeated clinical use.
In medical terminology, instruments are usually named according to:
Depending on their purpose, surgical instruments are divided into functional groups:
A key distinction in modern surgery is the level of tissue trauma. Atraumatic and minimally invasive instruments are designed to reduce tissue damage and improve patient recovery.
Diagnostic tools support the clinical examination of patients. Typical examples include reflex hammers, stethoscopes, otoscopes and measuring instruments for functional testing.
Surgical clamps temporarily occlude vessels or hold tissue securely during procedures. Different jaw geometries allow atraumatic fixation and controlled pressure distribution.
Examples include towel forceps, artery forceps and ligature clamps for safe hemostasis.
Needle holders ensure controlled needle guidance during suturing. Versions with tungsten carbide inserts increase grip durability and precision, especially for synthetic suture material and microsurgical procedures.
Surgical forceps are divided into toothed tissue forceps and atraumatic dressing forceps. They allow safe grasping of tissue, sutures or dressing material with minimal trauma.
An example is the anatomical dressing forceps used for delicate structures.
Puncture instruments create controlled access to body cavities. They include biopsy cannulas, trocars and suction tubes for fluid evacuation.
Specialized instruments can be found in plastic surgery instruments and liposuction cannulas.
Operating scissors are used for cutting materials and tissue, while dissecting scissors allow precise tissue preparation.
Specialized variants include eye and iris scissors for microsurgical procedures.
Scalpels provide precise incisions with different blade geometries depending on tissue type.
Scalpels and blades are available as reusable handles with disposable sterile blades.
Probes are used to examine wound channels, fistulas and cavities and to detect foreign bodies.
Retractors hold tissue apart to provide visibility in the surgical field. Self-retaining retractors maintain the operative opening without manual assistance.